Cholesterol Chronicles: Navigating the Balance for Heart Health and Well-being
Understanding Cholesterol: The Basics
Cholesterol is a fatty, wax-like substance that is found in all the cells of the human body. It plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including the production of hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids that aid in digestion.
It is also important to understand different types of cholesterol. The two main types of cholesterol are low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad cholesterol”, carries cholesterol to cells throughout the body. But it can also build up in the arteries, creating hinderance to carry blood to your heart and other body parts which increases the risk of heart diseases.
HDL cholesterol, often called “good cholesterol”, helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream and arteries and takes it back to the liver to be broken down into smaller components and eliminated from the body. High HDL cholesterol levels can help in lowering the risk of heart disease.
Good and Bad Cholesterol: What You Need to Know

Comparison of Good vs Bad Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol, also known as ‘good cholesterol’, helps in removing LDL cholesterol from the blood.
Therefore, high HDL cholesterol levels are beneficial for your health as it helps lowering the risk of heart disease.
Also, LDL cholesterol, commonly referred to as ‘bad cholesterol’, may increase the risk of heart diseases such as arteries blockage or high blood pressure.
LDL cholesterol tends to build up in the arteries, forming plaque and restricting blood flow.
Having an understanding about the difference in these two types of cholesterol is crucial for managing your cholesterol levels.
By keeping HDL cholesterol high and LDL cholesterol low, you can protect your heart from various diseases.
Recognizing Cholesterol Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
High cholesterol generally does not cause any immediate symptoms. Therefore, regular cholesterol tests are important. However, in some cases, there may be signs in the body which indicate high cholesterol levels. Here is a comprehensive guide to recognizing cholesterol symptoms:
Chest Pain

Chest pain or discomfort, also known as angina, could be a symptom of high cholesterol. This type of chest pain occurs due to blockage of arteries because of cholesterol build-up leading to reduced blood flow to the heart.
Yellowish Deposits on the Skin
High cholesterol can also cause yellowish deposits, known as xanthomas, to form on the skin.
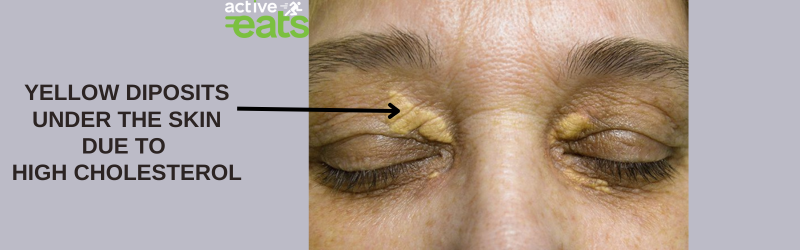
These deposits can be seen as wax-like deposits under the skin. They are usually seen on the tendons of the hands, feet, elbows, or knees of the person having high cholesterol levels in blood.
Nevertheless these symptoms are common indicators of high cholesterol, but these are also not exclusive to high cholesterol only and can also be caused by other conditions as well. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels: Why It’s Important
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is very essential for to identify any potential health risk related to heart and skin diseases. By monitoring your levels, you can:
Identify potential risks: Regular monitoring of can help in finding any abnormalities in LDL cholesterol, which can increase your risk of heart disease.
Guide treatment options: Early detection of high HDL cholesterol levels can help in opting for the best course of action to manage the cholesterol levels. The process may include lifestyle modifications, medication, or both.
Initiating Lifestyle Changes: By detecting high cholesterol levels, we can take initiatives for our lifestyle that might level in lowering the cholesterols and risks associated with high HDL cholesterols.
It’s also important to note that cholesterol levels can fluctuate; therefore, regular monitoring is key to ensure you’re aware of any changes and can take appropriate action.
Cholesterol Test: How It Works and What to Expect
A cholesterol test, also known as a lipid profile test, measures various types of cholesterol present in the blood.

The procedure includes simple blood test where a healthcare provider will typically take a blood sample and then send the sample to a laboratory to analyze the cholesterol levels.
The results of the cholesterol test will provide information about your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Total cholesterol is the sum of LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and 20% of your triglyceride level.

LDL cholesterol indicates the amount of cholesterols in our cells. Excess of LDL cholesterol can leads to build-up in heart arteries resulting in blockage.
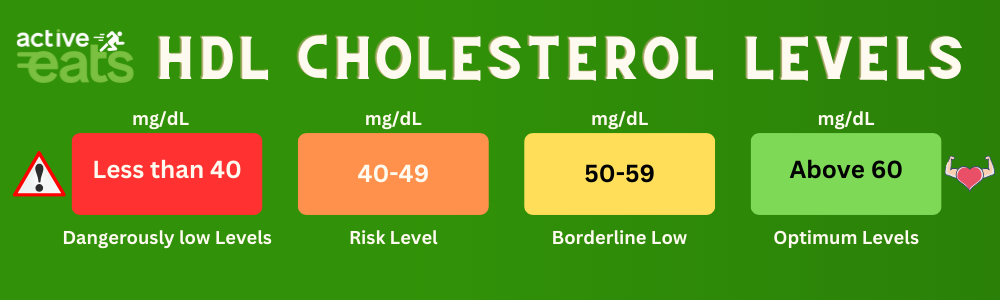
HDL cholesterol is the high density cholesterol that helps moving LDL cholesterol from cells and arteries to your liver. Therefore, high HDL is expected for healthy heart and skin.
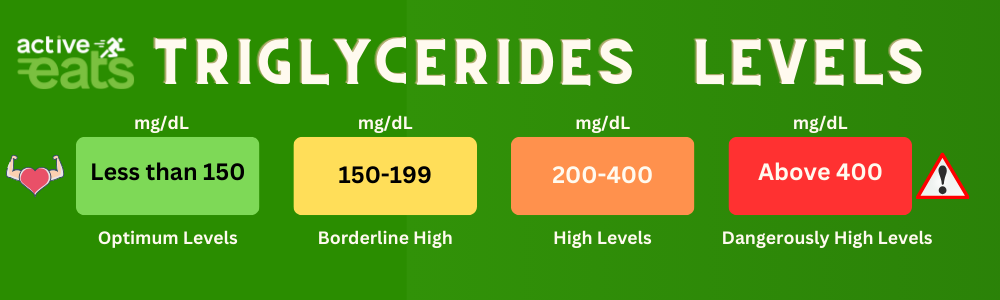
Triglycerides level in blood indicates the amount of unused calories your body have. This can also shed some light on our daily lifestyle. High triglycerides level indicates the intake of excess calories than required. This leads to deposition of fat in arteries.
The Effect of Cholesterol on the Heart: Exploring the Link

High LDL cholesterol levels can leads to the formation of wax like substance in the arteries. This causes the arteries to narrow and harden over time. This narrowing of blood vessels is known as atherosclerosis. It can hinder the natural flow of blood to the heart leading to various cardiovascular problems.
To reduce the risk of heart problems associated with high cholesterol, one must focus on adopting a healthy diet to increase HDL levels and maintain calorie intake.
The Impact of Cholesterol on Liver Health: What You Should Know
As the cholesterol levels increases in blood, liver cells get an abnormal build up of fat leading to fatty liver. This can impair liver function and potentially lead to complications.
In addition to managing the cholesterol levels, it is important to adopt a healthy lifestyle to support liver health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on liver health and overall well-being.
Statins for High Cholesterol

Statins are commonly prescribed medications that can help lower LDL cholesterol levels. It contain drugs that hinders a particular enzyme in the liver that contributes to cholesterol production. Therefore, statins can help lower LDL cholesterols and hence decreasing the plaque build up in heart arteries.
The most common side effects of statins include:
Muscle aches or weakness
Headaches
Stomach upset
Generally, statins do not have serious side effects but it’s overuse may lead to liver problems or an increased risk of developing diabetes.
Important Note: It is important to never stop taking statins without consulting your healthcare provider. Abruptly discontinuing statin therapy can have negative effects on your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
Cholesterol and Nuts: Exploring the Nutritional Impact

Nuts, such as almonds, pistachios, hazelnuts, macadamias, Brazil nuts and walnuts, have possess potential in managing cholesterol levels. These nuts contain healthy fats, which raises levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol which helps remove low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Almonds, for example, are rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been associated with increased HDL cholesterol levels. Studies have shown that including almonds in a balanced diet can contribute to improved cholesterol profiles.
Similarly, walnuts are a great addition to a cholesterol-friendly diet. They contain high levels of polyunsaturated fats, specifically omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to reduced LDL cholesterol levels and improved heart health.
Note: Nuts are high in calories, therefore, nuts should be taken in moderation to excessive calorie intake. A small handful of nuts per day, about 1.5 ounces, is typically recommended as a healthy portion size.
Incorporating nuts into your diet can be as simple as snacking on them raw or adding them to your favorite dishes. They can be sprinkled on salads, blended into smoothies, or used as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal. Get creative and enjoy the nutritional benefits of these heart-healthy snacks!
Exercise for Lowering Cholesterol: Effective Strategies and Tips
Regular physical activity can aid in managing cholesterol levels. Here are some effective strategies and tips for incorporating exercise into your routine:
Choose aerobic exercises: Aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling are particularly beneficial for lowering LDL cholesterol levels and raising HDL cholesterol levels.
Start slow and gradually increase intensity: If you’re new to exercise, start with low-impact activities and gradually increase the intensity and duration over time. This allows your body to adapt and reduces the risk of injury.
Include strength training: Incorporating strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help build muscle mass and improve overall cholesterol levels.
Make it a habit: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise every week. Consistency is key to reaping the benefits.
Remember, before starting any new exercise routine, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to ensure it’s safe for you, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Worst Foods for High Cholesterol: What to Avoid
Some food can directly increase your LDL cholesterol results in severe heart and liver issues. Therefore, certain foods should be avoided or consumed in moderation.

Fried Foods
Foods that are deep-fried or cooked in unhealthy oils are high in saturated and trans fats. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels, so it’s best to limit your consumption of fried foods like french fries, fried chicken, and onion rings.
Processed Snacks
Many processed snacks, such as chips, cookies, and crackers, are often loaded with unhealthy fats and added sugars. These snacks can raise LDL cholesterol levels and promote weight gain, which can further contribute to heart disease risk.
Fatty Meats
Fatty meats like bacon, sausage, and high-fat cuts of red meat are sources of saturated fats that can raise LDL cholesterol levels. Opt for lean cuts of meat and remove visible fat before cooking to reduce your saturated fat intake.
Butter and Full-Fat Dairy Products
Butter, cream, and full-fat dairy products like whole milk and cheese are high in saturated fats. These fats can increase LDL cholesterol levels, so consider choosing low-fat or skim versions of dairy products or using healthier alternatives like olive oil or avocado.
Baked Goods
Baked goods such as pastries, muffins, and cakes often contain unhealthy fats and added sugars. These foods can raise LDL cholesterol levels and contribute to weight gain. Opt for healthier alternatives like homemade baked goods using whole wheat flour, and reduce the amount of added sugar.
Fast Foods
Fast foods like burgers, fried chicken sandwiches, and hot dogs are typically high in saturated and trans fats. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and contribute to heart disease risk. Limit your intake of fast foods and choose healthier options whenever possible.
The Role of Cholesterol and Alcohol: Debunking the Myths
Myth 1: Alcohol is Good for Cholesterol:
Reality: There are no significant effects seen on cholesterol due to the consumption of alcohol. Also, there are more risks than benefits of alcohol consumption. Therefore, it’s not recommended to start drinking alcohol purely for cholesterol-related reasons.
Myth 2: Red Wine is the Only Beneficial Alcohol:
Reality: Red wine do contains certain antioxidants like resveratrol but the benefits of such antioxidants can also be obtained from other sources, such as grapes, blueberries, and certain nuts. The specific type of alcohol (e.g., red wine) isn’t the only way to gain these antioxidants.
Myth 3: Mixing Alcohol and Medications Doesn’t Matter:
Reality: Mixing alcohol with certain medications, including those prescribed for cholesterol management, can have adverse effects and may interfere with the medication’s effectiveness. Therefore, it is highly crucial that alcohol and medications should not be mixed together.
Myth 4: Alcohol Helps Manage Stress and Cholesterol:
Reality: While alcohol might provide temporary relief from stress, but it’s definitely not a healthy or long-term solution.
Cholesterol and Stress: Unravelling the Connection
Stress is directly linked to cholesterol level in human body. Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can affect how the body metabolizes fats and sugars. This can lead to higher levels of LDL cholesterol.
Also, people under stress might engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating, consuming comfort foods high in unhealthy fats and sugars, and avoiding exercise. Such behaviour can negatively impact cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Changes and Diet to Improve Cholesterol: Practical Tips
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels involves making important lifestyle changes and adopting a nutritious diet. Here are some practical tips to help improve your cholesterol levels:
- Incorporate more fruits and vegetables
Fill your plate with a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are rich in fiber and antioxidants. These nutrients can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
- Choose whole grains
Opt for whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat bread, and quinoa instead of refined grains. Whole grains contain more fiber, which can help reduce cholesterol levels.
- Include lean proteins
Choose lean sources of protein, such as skinless chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes. These options are lower in saturated fats and can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Limit saturated and trans fats
Avoid foods that are high in saturated and trans fats, such as fatty cuts of meat, full-fat dairy products, and fried foods. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Opt for healthy fats
Include foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts, in your diet. These fats can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and promote overall heart health.
- Increase fiber intake
Eat more fiber-rich foods like legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Fiber can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve digestive health.
- Limit processed foods
Avoid processed snacks, fast food, and packaged meals that are often high in trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. These foods can negatively impact cholesterol levels and overall health.
- Watch your alcohol intake
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise triglyceride levels and increase the risk of high cholesterol. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation and limit intake to one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men.
- Quit smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and can lower HDL cholesterol levels. Quitting smoking can improve cholesterol and overall cardiovascular health.
- Manage stress
Chronic stress can affect cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. Practice stress-management techniques like meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
Managing cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of heart disease. Understanding the different types of cholesterol and their effects on the body is the first step in maintaining optimal levels. Regular monitoring crucial for identifying potential risks and guiding treatment options.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and raise HDL cholesterol levels. Incorporating nuts into your diet, engaging in aerobic exercise, and avoiding foods high in saturated and trans fats are all effective strategies for managing cholesterol.
By making these changes and implementing healthy habits, you can improve your cholesterol levels and promote overall cardiovascular health. Taking proactive steps towards managing cholesterol is an investment in your long-term well-being.