Unveiling the Weighty Matter: Understanding and Confronting the Complexities of Obesity
Millions of people around the world are affected by obesity. It is a condition when our body begins to store too much body fat, resulting in adverse effects on our overall health and well-being. In this blog post, we will learn about the various aspects of obesity, primary causes, early signs, and effects of obesity on our daily life. Also, we will learn about various methods to combat obesity, as well as the health issues associated with obesity.
Types of Obesity

- Android Obesity or Central Obesity: Android obesity occurs when excess fat starts accumulating around the abdominal region, resulting in an apple-shaped body. Hence, it is also known as apple shaped obesity. It is generally seen in men and postmenopausal women due to hormonal changes. It increases the risk of developing chronic diseases and metabolic disorders.

- Gynoid Obesity or Peripheral Obesity: Gynoid obesity occurs when fat accumulation occurs in the lower body, particularly around the hips and thighs, giving rise to a pear-shaped body. It is generally seen in women due to hormonal factors such as estrogen levels and genetic predisposition.

- Visceral Obesity: Visceral obesity, also known as hidden fat, is the excess fat stored deep within the skin, around vital organs like the liver, pancreas, and intestines. It is commonly found in individuals with android obesity but can also occur independently. Visceral fat affects our body metabolism as it produces inflammatory substances that contribute to insulin resistance, high blood pressure and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.

- White Adipose Tissue (WAT) Obesity: White adipose tissues store excess energy in our cells in the form of triglycerides. White Adipose tissue (WAT) obesity occurs when our calorie intake is higher than the calories used by our body. White adipose tissues are present throughout our body as visceral fat and bone marrow fat. Excessive WHAT tissue can result in obesity and other health related issues.

- Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) Obesity: Brown adipose tissues are darker in colour and less common. They are generally found around the back, neck and shoulder. Brown fat cells burn calories to generate heat. Accumulation of too many brown fat cells can lead to impaired thermogenesis (heat production) and reduced calorie expenditure.
Genetic factors of obesity
Although genetics alone cannot direct a person towards obesity, it indeed plays a crucial role in identifying individuals who are more susceptible to obesity.
The FTO Gene: The Fat Mass and Obesity (FMO) is the first gene found that is associated with obesity. It makes people inclined towards eating high calorie foods and overeating. It also affects our brain’s reward system and hunger signals.
Leptin Resistance: Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that regulates appetite. When our body becomes leptin resistant, it does not respond to leptin as it would normally do, resulting in overeating and not feeling the sense of fullness.
MC4R Gene Mutations: A rare gene mutation is found to be one of the common causes of intense obesity. People with mutation with their Melano Cortin 4 Receptor (MC4R) gene often experience an insatiable appetite from early childhood and struggle with maintaining a healthy weight throughout their lives.
Role of lifestyle choices in obesity: Causes of Obesity
- Sedentary Lifestyle: When a person spends six or more hours at an almost static position like sitting, lying on bed, then such a lifestyle is known as sedentary lifestyle leading to obesity. A typical office worker spends most of his time sitting at desks or engaging in minimal physical activities. Leading such a lifestyle for long can result in increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders.
To combat this, individuals should incorporate regular exercise into their daily routines. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, or joining fitness classes can help burn calories and reduce abdominal fat accumulation.
- Unhealthy Diet: Eating unhealthy diet in the form of sugary drinks, processed foods high in saturated fats and added sugars can lead to weight gain. No matter how much physical you engage yourself in, without a healthy and clean diet you cannot achieve your fitness goals.
To address this issue, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential. Portion control and mindful eating practices can also help prevent overeating and promote weight management.
- Sleep Deprivation: One of the major factors for obesity is lack of adequate sleep. Sleep deprivation may affect natural hormone balance in your body leading to increased hunger cravings and decreased energy expenditure.
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule with 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Also, reducing screen time before bed could be one of the best decisions for a healthy and sound sleep.
- Stress and Emotional Eating: Stress contributes to increased cortisol in our body. This increase in cortisol increases appetite and craving for sugary and calorie rich foods resulting in increased weight.
Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help alleviate stress and reduce emotional eating tendencies.
Conclusion: Understanding the role of lifestyle choices in differentiating types of obesity is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, and managing stress effectively, individuals can reduce their risk of developing obesity and its associated health complications.
Early Signs of Obesity
There are various physical and psychological indicators that may signal the start of obesity.
Physical Indicators
One of the primary ways to check for obesity is body mass index (BMI). This can be assessed by measuring your weight and height and calculating your BMI.
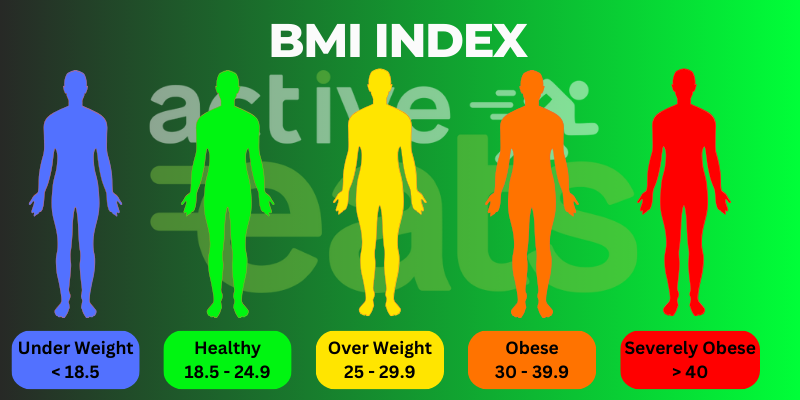
BMI Index gives a general idea about your fitness level; however, it is believed that BMI is a bit flawed. IT does not consider factors such as age and sex. Also, it does not distinguish between body fat mass, muscle mass or bone density which plays a crucial role in determining fitness levels.
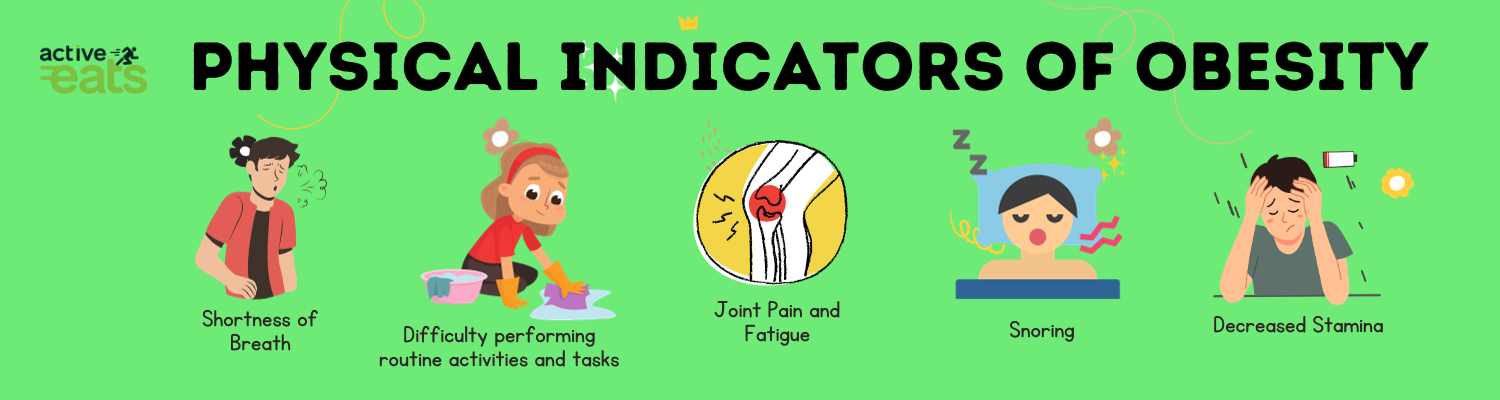
Other physical indicators of obesity include:
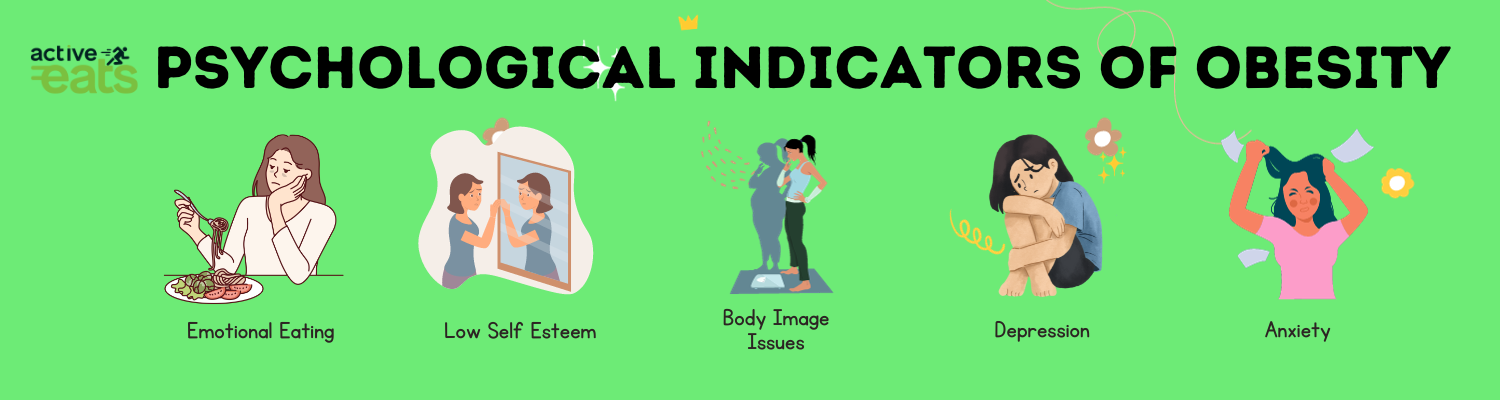
Psychological Signs of Obesity:
While obesity primarily affects physical health, it can also have psychological implications. Some psychological signs that may be early indicators of obesity include:
Although these signs may vary from person to person, they give a clear indication about our health condition. If you notice any of these signs, it is advisable to consult with a medical professional for an accurate assessment and appropriate advice.
Effects of Obesity on Our Daily Life
Obesity not only affects our physical health but also our mental well-being and social interactions.
- Impact on overall mobility and physical activities
One of the immediate effects of obesity is the difficulty in mobility and physical activities. Excess weight of our body puts more strain on our joints making it difficult to move comfortably. This results in difficulty in simple activities like walking or climbing stairs.
- Strain on mental health and Social implications
Obesity can take a toll on our mental health and well-being. Obesity can make us conscious about our body image and can lead to low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety. Also, obese people also face discrimination and stigma, which further contributes to psychological distress and social isolation. Also, they may also face negative stereotypes and biases which might affect their personal relationships, employment opportunities, and overall quality of life.
Overall, obesity has far-reaching effects on our daily life, impacting our physical abilities, mental well-being, and social interactions. It is important to address obesity not only for its health implications but also to foster a society that promotes acceptance and understanding.
Obesity: Preventive Steps to Be Taken
Preventing obesity is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some practical steps that can be taken to prevent obesity:
Adopt a Balanced Diet: Consuming a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help in avoiding obesity. Also, limiting the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and high-calorie snacks can assist in preventing obesity and other related health issues.
Incorporate Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activities for at least 15 to 20 minutes daily such as walking, jogging, swimming, or dancing can help in burning excess calories and maintain the right amount of fat in the body.
Maintain Portion Control: Be mindful of your portion sizes and avoid overeating. Try to consume a calorie deficit diet and follow a disciplined lifestyle. You can install a calorie tracker application in your phone that may help in tracking calories of your daily food intake.
Limit Sedentary Lifestyle: Reduce the amount of time spent sitting or being inactive. Include more movement throughout your day by taking regular breaks to stretch, standing up during phone calls, or taking the stairs instead of the elevator.
Get Sufficient Sleep: Lack of sleep is the main cause of disturbed appetite-regulating hormones. Therefore, aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Also, try to avoid mobile or blue light 2 hours before bed.
Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to cope with stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from friends and family. Stress can contribute to emotional eating and weight gain.
By incorporating these preventive steps into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of obesity and its associated health complications.
Obesity and Diabetes
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When a person gains excessive body fat due to obesity, the body develops insulin resistance. Pancreas tries to compensate for this insulin resistance of the body by producing more insulin. Over a long time, when pancreas are not able to compensate for enough insulin for the insulin-resistant body then the blood sugar level begins to rise leading to the development of diabetes.
Managing obesity is crucial in preventing and managing diabetes. Weight loss through a combination of a balanced diet, regular physical activity and proper sleep can improve insulin sensitivity and lower the risk of developing diabetes.
Morbid Obesity
Morbid obesity is a severe form of obesity that is characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat to the extent that it poses a significant risk to health. It is usually defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher.
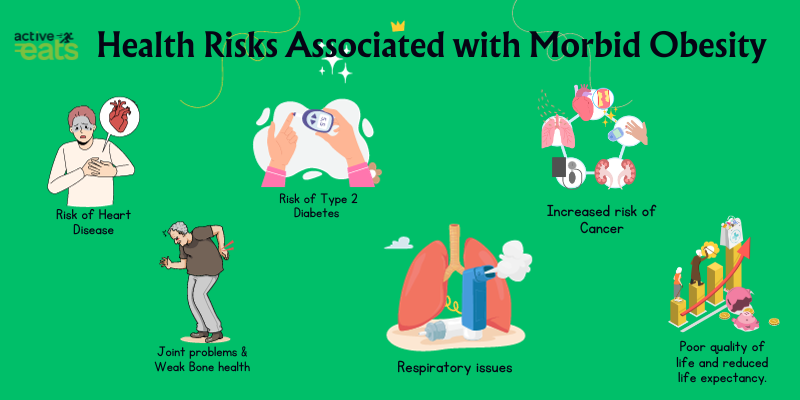
Individuals with morbid obesity face numerous health risks and complications. These can include:
Managing morbid obesity often requires a comprehensive approach. Treatment options for person suffering from morbid obesity may include:
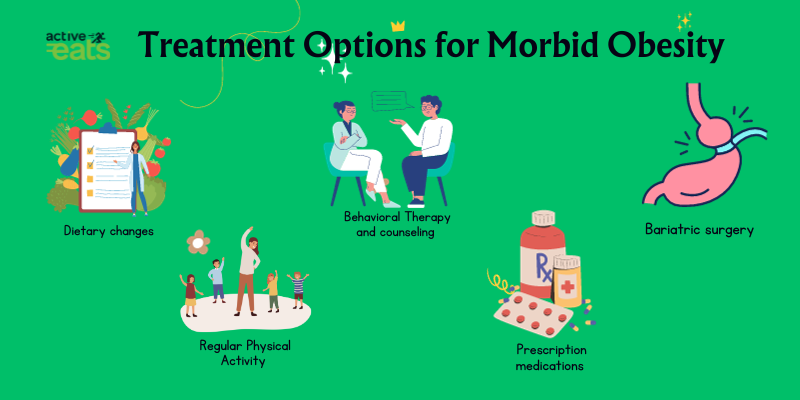
It’s important to seek medical advice and support when dealing with morbid obesity, as it can significantly impact both physical and mental well-being.
Obesity Rates by Country
Obesity rates vary significantly across different countries, highlighting the global concern surrounding this health issue.
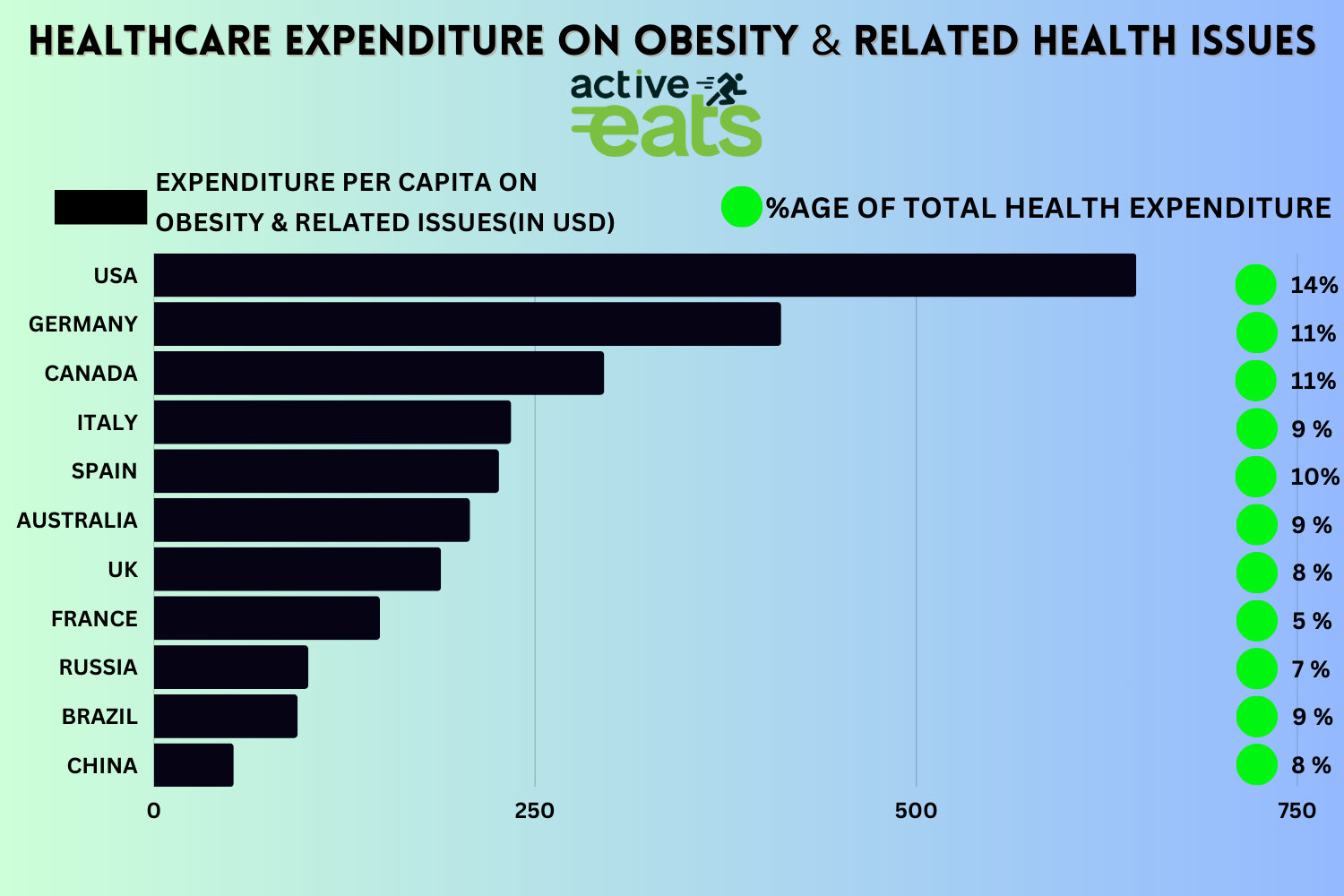
Understanding these rates can shed light on the cultural, socioeconomic, and environmental factors influencing the prevalence of obesity.
Reason for Variations in Obesity Rates
The reasons for huge variations in obesity rates of countries are multifaceted and include factors such as dietary habits, physical activity levels, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare.
For example, countries with a higher prevalence of fast food consumption and sedentary lifestyles tend to have higher obesity rates.
On the other hand, countries that prioritize healthy eating habits and physical activity tend to have lower obesity rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, obesity is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects individuals all over the world. Understanding the different types of obesity, including their characteristics, genetic factors, and lifestyle choices, is crucial in addressing this epidemic. Primary causes of obesity, such as excessive calorie intake, sedentary lifestyles, genetics, and hormonal factors, play a significant role in its development.
Obesity leads to various health issues, including an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases and respiratory problems. The link between obesity and chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension is well-established. Managing weight and improving insulin sensitivity through lifestyle modifications are crucial in preventing and managing obesity-related diabetes.
For individuals with morbid obesity, understanding the potential health risks and exploring available treatment options are of utmost importance. Comparing obesity rates across countries sheds light on cultural, socioeconomic, and environmental factors influencing this issue, and allows for informed public health policies.
In conclusion, addressing obesity requires a comprehensive approach that includes education, awareness, preventive measures, and accessible treatment options. By taking action at the right stage and making informed choices, individuals and societies can work together to combat obesity and improve overall health and well-being.

Deceptive Depression : What You Need to Know | Coach Active Eats
[…] Obesity […]