Mastering the Art of Quality Sleep: A Comprehensive Guide to Transform Your Health and Well-Being
Sleep and health are two sides of a same coin as sleep impacts both our mental and physical health. It affects our metabolism along with our body’s ability to fight against diseases and develop good immunity. In this blog post, we will delve into the numerous benefits of good sleep, explore the different stages of sleep, and uncover the impact of sleep on our health. By the end, you will have a better understanding of why sleep is essential and how it can significantly improve your overall well-being.
Why Sleep is Important: Uncovering the Importance of Quality Rest

A good quality of sleep is highly crucial for our mental as well as physical well being. Lack of proper sleep can leads to disturbed metabolic rates, increased body weight, high stress and low immunity. Getting enough sleep is crucial for optimum brain performance. Sleep deprivation can increase the risk of chronic diseases like obesity and diabetes. Establishing a healthy sleep routine can help in improving overall quality of life.
Unlocking the Benefits of a Good Night’s Sleep

Adequate sleep improves memory and brain performance. When we read or study during day, our brain stores that information in a random manner. When we sleep, our brain consolidates and organizes that information in an easy-to-recall manner, making it easier for us to retain most of the information learned during the day.
Also, a good sleep promotes creativity and problem-solving skills. During sleep, our brain gets rewired, helping us come up with innovative solutions to problems. It helps us in looking at problems from other perspectives.
Quality sleep is linked to better productivity and focus throughout the day. When we wake up well-rested, we feel increased energy and improved concentration in our body resulting in enhanced cognitive function which allows us to be more productive and focused throughout the day.
Getting enough sleep also boosts enhance athletic performance and muscle recovery. During sleep, our body repairs the damaged muscle tissues which help them grow, and our bodies replenish energy stores in cells, leading to improved athletic performance and quicker recovery from physical exhaustion.
Sleep is also crucial for hormonal regulation and maintaining a healthy weight. Lack of sleep can create imbalance in various hormones leading to increased cravings for unhealthy foods and weight gain. On the other hand, getting enough sleep helps maintain a healthy metabolism and promotes weight management.
Sleep and Health: Mental and Physical Health
Quality sleep is associated with improved mental health and emotional well-being.
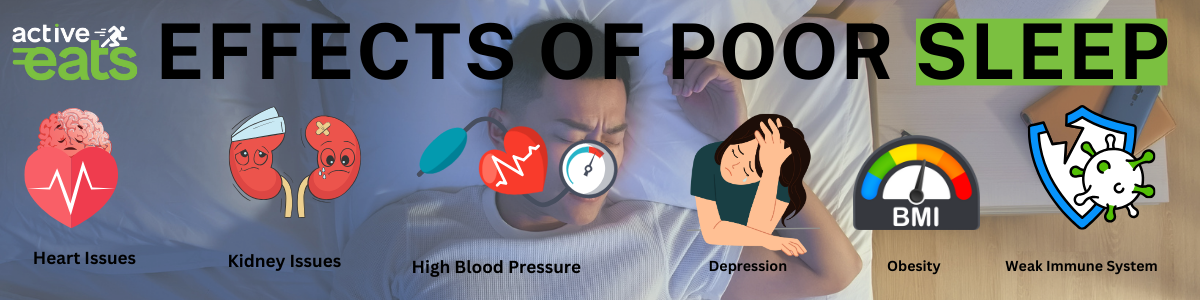
Poor sleeping patterns can lead to many chronic health issues related to heart issues, kidney issues, high blood pressure, diabetes, depression and obesity.
Lack of sleep can contribute to the development of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. Sleep deprivation weakens the immune system and can lead to chronic body pain. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule can help regulate mood and improve cognitive function.
Lack of sleep also affects our brain’s ability to process complex thoughts leading to confusion and decreased ability to take decisions. Long term effects of poor sleep can result in severe depression and lack of ambitions in life.
Hence, a good sleep affects almost all aspects of our health.
Exploring the Different Stages of Sleep and Their Significance

During sleep, our eyes move rapidly in random directions but do not sends any visual information for brain to process. This random rapid eye movement is known as REM (Rapid Eye Movement). And the duration when our eyes do not perform any rapid movements is known as NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement).
Our Sleep cycle consists of four main stages: NREM 1, NREM 2, NREM 3, and REM.
As soon as we feel asleep, we enter into NREM stages followed by a shorter REM stage. And this cycle repeats continuously during our whole sleeping time.
Each sleep stage plays a crucial role in restoring and rejuvenating the body. REM sleep is associated with dreaming and sorting and organizing memories and information. While NREM sleep is important for physical growth, tissue repair, and hormone release. Understanding the different sleep stages can help optimize sleep quality and health.
NREM Sleep:
NREM sleep is the initial phase of sleep and comprises approximately 75-80% of the total sleep cycle.
It can be further divided into three stages: NREM 1, NREM 2, and NREM 3 (also known as slow-wave sleep or deep sleep). Each stage lasts between 5 to 25 minutes.
NREM 1 Stage: When we close our eyes to go to sleep, we enter into NREM 1 stage where we feel slow drifting sensation. This is a light sleep stage which may last for 5 to 10 minutes.
NREM 2 Stage: In this stage, our body and mind fall into slow sleep state where our brain waves become slower with occasional bursts of rapid waves called sleep spindles. Our heart rate and body temperature drop in this stage. It lasts for 15 to 25 minutes and constitutes a significant portion of total sleep time.
NREM 3 Stage: This is the deepest stage of NREM sleep, characterized by slow, large-amplitude brain waves known as delta waves. In NREM 3 stage, it is difficult to wake up and if we do, we may feel slight disoriented for some time. This stage is essential for physical growth, muscle repair, immune system support, and overall well-being.
REM Sleep:
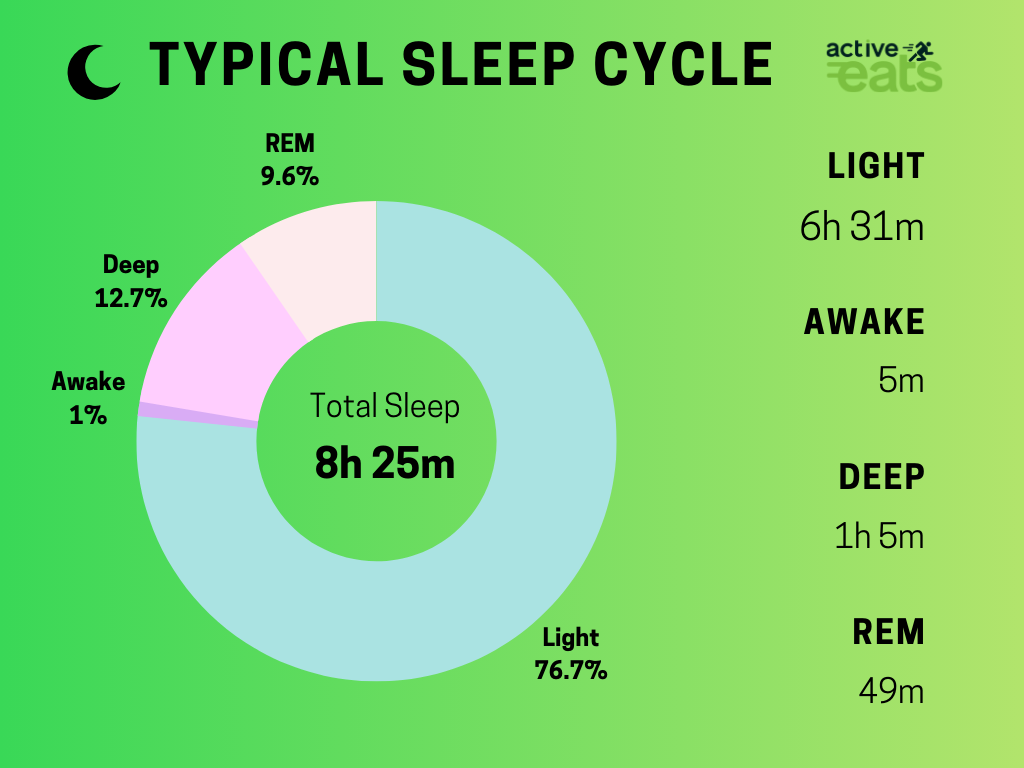
REM sleep usually occurs after a cycle of NREM sleep and accounts for approximately 20-25% of the sleep cycle, becoming longer as the night progresses.
During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, and most dreaming occurs in this stage only. Also, REM sleep helps in organizing the thoughts and information stored in our brain. Disturbed REM sleep may leads to confusion and depression.
In this stage, rapid eye movements occur along with enlightened heart rate and breathing become irregular. The body undergoes a type of paralysis during REM sleep, known as REM atonia, which prevents individuals from acting out their dreams.
REM sleep is linked with cognitive processes, memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and creative thinking.
REM sleep occurs 90 minutes after falling asleep and may last 10-15 minutes. With each sleeping cycle, REM stage gets longer and the final one may last up to one hour. Babies spend more than half of their sleep in REM stage as compared to adults who spend less than one fourth of total sleep time in REM stage.
As the night progresses, the proportion of REM sleep increases, while the proportion of deep NREM sleep decreases.
Sleep and Heart Health: How Your Rest Habits Affect Your Cardiovascular Wellbeing
Getting enough sleep is important for maintaining a healthy heart and reducing the risk of heart disease. Sleep deprivation can increase blood pressure and heart rate, putting strain on the cardiovascular system.
Lack of quality sleep is associated with an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Establishing a regular sleep schedule can help regulate blood pressure and promote heart health. Improving sleep habits can have significant benefits for overall cardiovascular wellbeing.
Sleep Disorders
Lack of sleep may not only lead to poor mood and lack of judgment abilities but also effects our sleeping patterns. People who use drugs or alcohol leads to shorter NREM stages resulting in quick advancing towards REM stage. This disturbs the temporary paralysis stage of REM cycle leading to acting out or speaking in response to the dream or nightmare.
Long term REM sleep disorders can lead to serious mental conditions like Parkinson disease or dementia.
Bedtime Routine
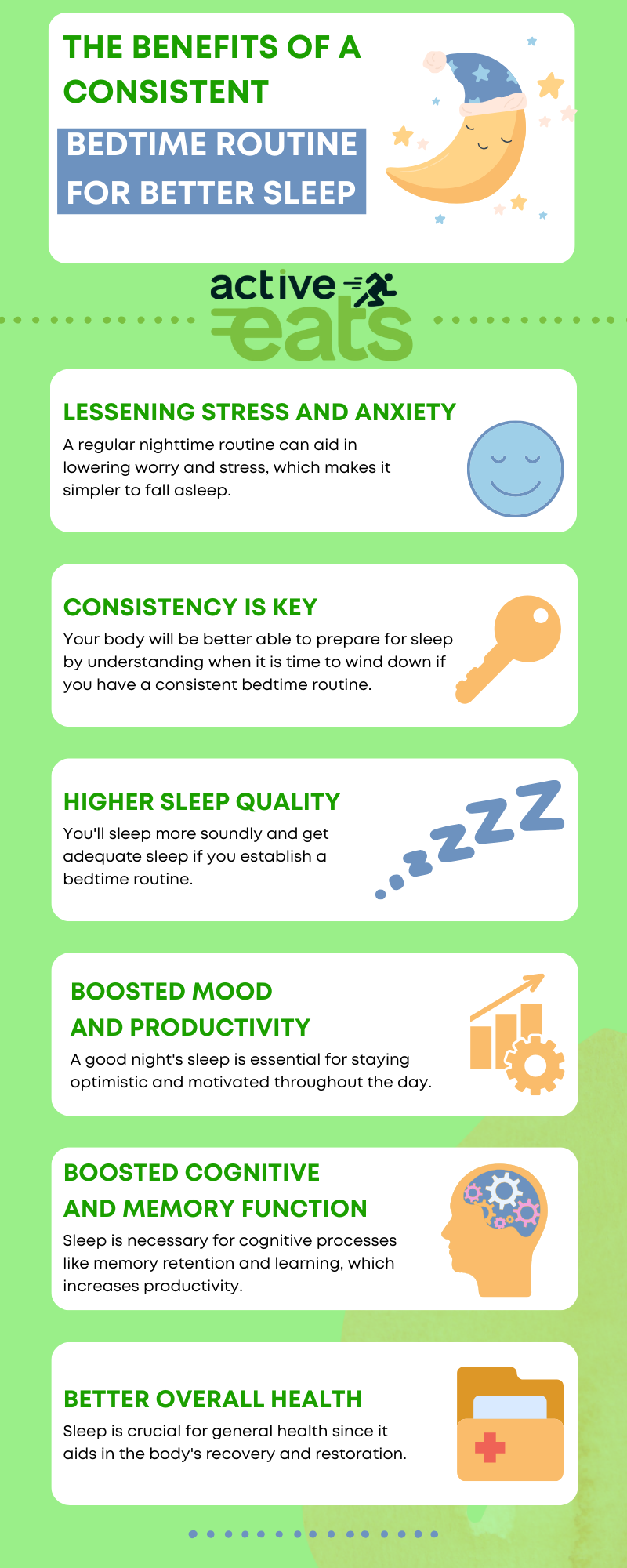
A bedtime routine signals the body and mind that it’s time to sleep which helps the body to get into relaxed state easily. It can include calming activities like reading or gentle stretches, reducing stress and anxiety. Consistent routines regulate the body’s internal clock, leading to more regular sleep patterns. For children, bedtime routines are particularly essential, fostering a sense of security and comfort. They can enhance parent-child bonding and promote healthy sleep habits. Overall, a bedtime routine supports better mental, emotional, and physical well-being by facilitating relaxation, better sleep, and stress reduction.

Conclusion
Sleep plays a vital role in our overall mental as well as physical health. Lack of sleep can have negative effects on cognitive function; mood, immune system function, and can increase the risk of chronic diseases like obesity and diabetes. On the other hand, getting enough quality sleep has numerous benefits, including improved memory, creativity, productivity, and athletic performance. It is also crucial for proper hormone balance and maintaining a healthy weight.
Additionally, sleep has a significant impact on mental health, with insufficient sleep contributing to the development of disorders like depression and anxiety. It is important to understand the different stages of sleep and their significance in order to optimize sleep quality and overall health. Sleep also plays a crucial role in heart health, with sleep deprivation increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. Establishing a healthy sleep schedule can help regulate blood pressure and promote heart health. In conclusion, prioritizing sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits can greatly improve our well-being and quality of life.


Top 6 Astounding Health Effects of Technology - Coach Active Eats
[…] health effect of technological overuse can be seen in our sleep patterns. The use of technology before bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns and negatively affect the quality […]
Healthy Lifestyle | Coach Active Eats
[…] Getting Enough Sleep […]
code of destiny
I am extremely inspired with your writing talents as neatly as with the format for your weblog. Is that this a paid topic or did you modify it yourself? Either way keep up the excellent quality writing, it is rare to peer a nice blog like this one today!