Inhaling Shadows: Unraveling the Harsh Realities – Side Effects of Smoking on Your Health
Smoking is a widespread common habit of individuals nowadays that comes with serious health consequences. The side effects of smoking on the body are severely negative and understanding these effects is crucial in order to make informed decisions about our health. In this blog post, we will explore the various ways in which smoking is impacting our health and discuss the importance of quitting this deadly habit. From the damage it causes to our lungs and heart to its connection with diabetes and depression, we will discuss its deteriorating effects and shed light on the hidden dangers of passive smoking too.
Additionally, we will explore alternatives to smoking for those who are trying to quit smoking but could not be able to do so. Also, alternative methods of smoking such as smokeless tobacco and e-cigarettes will also be discussed in this article. Ultimately, the goal of this blog post is to provide valuable insights into the impact of smoking on our health and to encourage and support those who wish to quit smoking for good.
The Side Effects of Smoking Tobacco: What Happens When You Smoke
When we smoke a cigarette, more than 5000 types of chemicals present in tobacco and nicotine burns and produces smoke that we inhale into our lungs. Out of these different chemicals present in cigarettes, atleast 50 of them are known to cause cancer. Some of the chemicals get burned completely while some gets burned partially.
As you inhale this smoke, some of the particles stick with your nose linings and air pipe causing irritating and cough. These chemical particles disturb the pH of your saliva resulting in decrease in good bacteria in your mouth which helps digesting food. This decrease in good bacteria also causes bad breath. Long term smoking causes tar to accumulate near tooth roots and gums leading to teeth discolouring and lips darkening.
The partially burned tobacco contains higher concentration of nitrogen oxides, ammonia, carbon monoxide, and tar – all very harmful substances. They get absorbed in our blood through lungs leading to increased pulse and heartbeat while tar, a thick paste present in very small quantity in cigarette smoke, doesn’t get absorbed into the blood. Hence, tar keeps on accumulating in the lungs which can cause lung diseases such as emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
When carbon monoxide gets absorbed, it reduces the oxygen carrying ability of blood cells. While tar which does not cause cancer is a highly addictive substance which triggers brain’s feel-good hormone. Many other harmful chemicals present in cigarettes cause direct harm to our DNA which results in abnormal behaviour of our immune system. Also, these harmful chemicals affects cell repairing mechanism which can leads to growth of cancerous cells resulting in health issues such as lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory problems.
Harmful Chemicals present in a Cigarette

Cigarette contains more than 5000 harmful chemical substances. Some of them are:
- Nicotine: Highly addictive, it raises heart rate and blood pressure.
- Tar: A carcinogenic substance that accumulates in the lungs.
- Carbon Monoxide: Reduces oxygen-carrying capacity of blood.
- Formaldehyde: A potent irritant and carcinogen.
- Benzene: A known carcinogen linked to leukemia.
- Arsenic: A toxic heavy metal associated with cancer.
- Ammonia: Enhances nicotine absorption, but is harmful to respiratory health.
- Hydrogen Cyanide: A poisonous gas that damages cells.
- Acetone: Found in nail polish remover and a respiratory irritant.
- Lead: Toxic heavy metal harmful to various organs and systems in the body.
Why people feel Pleasure in Smoking

The main reason people enjoy smoking is smoke and nicotine. As soon as nicotine dissolved in blood reaches brain, it causes brain to release adrenaline and dopamine hormone which gives a sense of pleasure and energy for the moment.
Also, along with the feeling of momentarily happiness people get with nicotine, smoke or the dense fumes of gases that people exhale while smoking cigarette is also one of another reason people smoke. There is a false trend nowadays of looking cool while smoking is going on probably from the movies. This makes individuals, especially teenagers, to try to act cool while smoking in the manner that they think is cool. This is one of the reason people try sheeshah or hookah which tends to give much denser cloud of smoke.
Smoking and its Connection to Diabetes
Smoking is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, increasing the chances of developing the disease. Research has shown that smokers have a 30-40% higher risk of developing diabetes compared to non-smokers.
Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone which helps glucose from food to enter into the blood cells in the right amount. Also, insulin triggers liver to store excess blood sugar for future use. When you smoke, nicotine gets dissolved in blood which hinders the normal functioning of insulin leading to increased levels of blood sugar increasing risk of diabetes. Prolonged smoking can result in insulin insensitivity resulting in serious organ damage.
Smokers with diabetes also have higher risks of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Smoking can affect insulin sensitivity and impair glucose regulation, contributing to the development of diabetes.
Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for individuals with diabetes. It can improve blood sugar control, reduce insulin resistance, and decrease the risk of diabetes-related complications. Therefore, quitting smoking is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively.
The Impact of Smoking on Heart Health

Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, increasing the chances of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage blood vessels, leading to the build-up of plaque and the narrowing of arteries leading to high blood pressure and heart rate, putting additional strain on the heart.
Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Smoking and Elevated Blood Pressure
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for developing elevated blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Hypertension is a condition in which the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high, putting extra strain on the heart and blood vessels. Over time, this can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.

Smoking causes the blood vessels to narrow or constrict. This narrowing of the blood vessels leads to increased hindrance to blood flow, which in turn raises blood pressure.
Smoking can increase the heart rate, making the heart work harder to pump blood. This can raise blood pressure over time.
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the arteries, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup. Plaque buildup can narrow the arteries and further contribute to high blood pressure.
Smoking is associated with increased inflammation throughout the body. Inflammation can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and high blood pressure.
Smoking activates the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response leading to increased blood pressure as the body respond to stress.
It’s important to note that the effects of smoking on blood pressure can vary from person to person, and not everyone who smokes will develop hypertension. However, quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of developing high blood pressure and its associated health complications.
Smoking and Depression: The Psychological Aspects

There is a strong link between smoking and depression, with smokers being more likely to experience depressive symptoms.
Nicotine in cigarettes can temporarily give relief from feelings of stress and sadness. This temporary feeling dry out quickly resulting in next urge to smoke again. This creates a cycle of dependence and worsening mental health.
Smoking cessation can improve symptoms of depression and enhance overall mental well-being. Treating nicotine addiction alongside depression can lead to better outcomes for individuals.
The Hidden Dangers of Passive or Second-hand Smoking

Passive smoking, also known as second-hand smoking, can be harmful to non-smokers who are exposed to tobacco smoke.
Exposure to passive smoke is considered more dangerous as smoke from unburned or partially burned tobacco particles are inhaled by passive smokers while active smokes inhale completely burned smoke as well as partially burned smoke. This partially or unburned smoke increases the risk of respiratory infections, asthma, and even lung cancer in non-smokers.
Children exposed to second-hand smoke are more prone to developing respiratory problems and experiencing impaired lung function.
Smoking and its Effects on the Brain

Smoking has negative effects on brain health, increasing the risk of cognitive decline and impairing memory and concentration. The harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke can damage brain cells and reduce the flow of oxygen to the brain. This damage can lead to difficulties with thinking, understanding, and problem-solving.
Furthermore, smoking degenerates brain cells quickly leading to disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. These diseases can result in a loss of memory, cognitive abilities, and overall functioning.
However, the good news is that quitting smoking can have remarkable benefits for brain health. Research has shown that quitting smoking leads to improvements in cognitive function and a reduced risk of brain-related diseases. Over time, the brain can repair and regenerate itself, allowing for better memory, concentration, and overall brain function.
Therefore, quitting smoking is not only beneficial for your physical health but also for your brain health. It can help protect against cognitive decline and improve your mental well-being in the long run.
Quitting Smoking: What Happens When You Quit and How to Quit Successfully
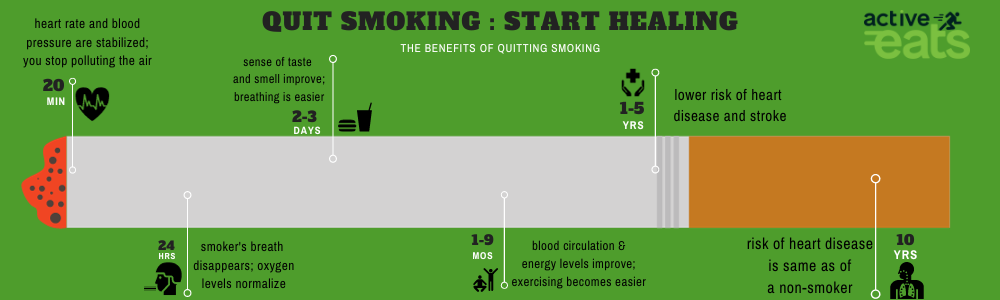
When you quit smoking, your body begins to heal. Lung function improves, circulation increases, and the risk of heart disease decreases.
Withdrawal symptoms may occur when quitting smoking, but they are temporary and can be managed with support and medications.
Quitting smoking is a process that may involve multiple attempts, but each attempt can bring you closer to success. Having a support system, setting a quit date, and adopting healthy coping strategies can increase the chances of successfully quitting smoking.
Exploring Alternatives: Smokeless Tobacco, E-cigarettes, and Vaping

Smokeless tobacco products, such as chewing tobacco and snuff, still pose health risks and can lead to oral cancers, gum disease, and nicotine addiction.

E-cigarettes, or vaping devices, are not risk-free and can expose users to harmful chemicals, including nicotine and other toxins. While they may be marketed as a safer alternative to smoking, the long-term health effects of e-cigarettes and vaping are not healthy.
Quitting tobacco and nicotine altogether is the best way to protect your health and reduce the risks associated with smoking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, smoking has numerous negative effects on health, ranging from lung cancer and respiratory problems to heart disease and cognitive decline. It is not only detrimental to the smoker but also to those exposed to second-hand smoke. Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for individuals, including improved lung function, reduced risk of heart disease, and enhanced mental well-being. However, it is important to note that alternatives such as smokeless tobacco, e-cigarettes, and vaping still carry health risks.
The best way to protect your health is to quit tobacco and nicotine altogether. Remember, quitting smoking is a process that may involve multiple attempts, but with the right support and strategies, it is achievable. Take charge of your health and make the decision to quit smoking today.

